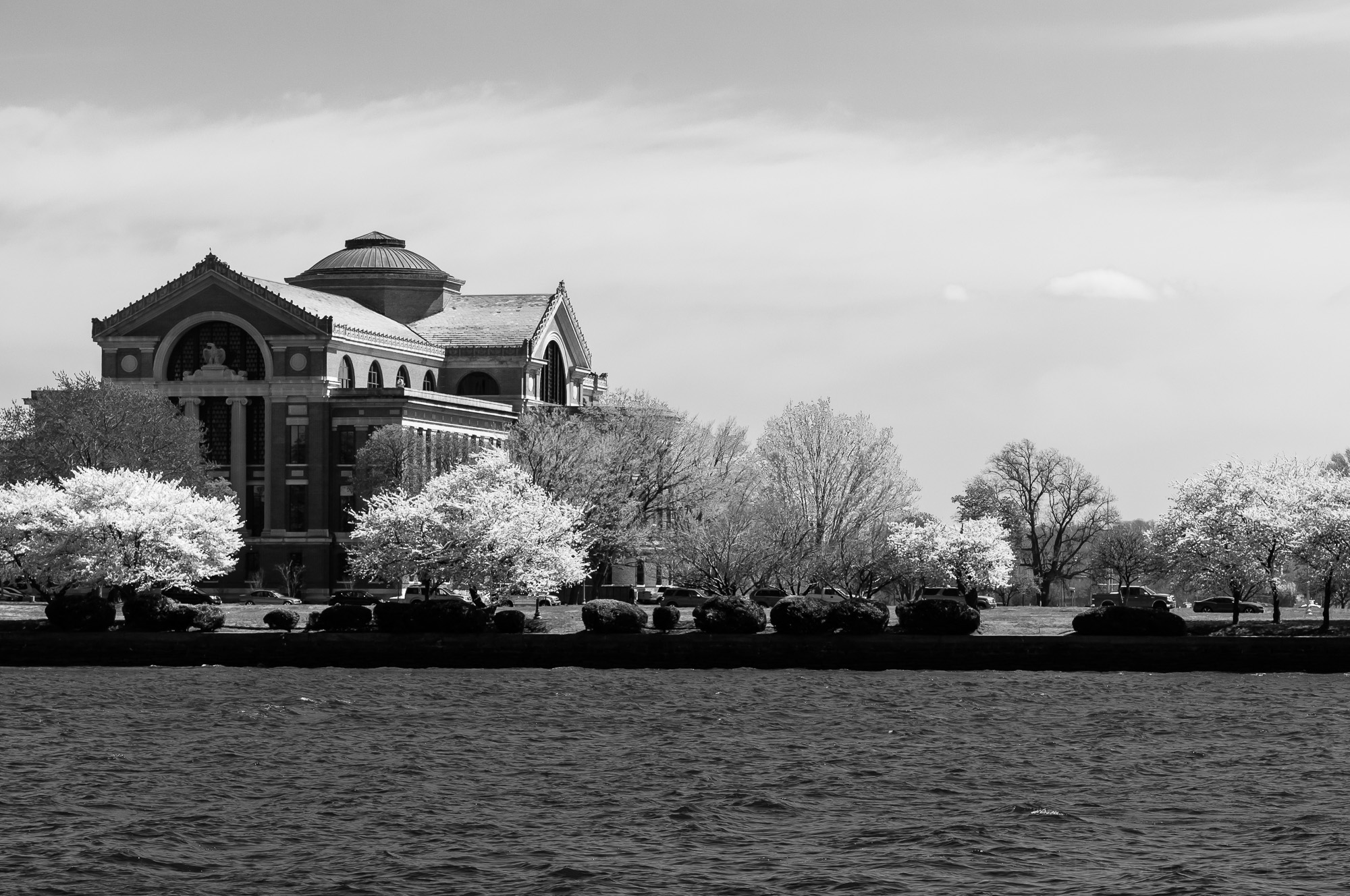
Black and white infrared composite image of the National War College, taken from East Potomac Park, Washington, D.C.
There are times you may not be able to capture the image you visualize in a single photograph. But you may be able to achieve your aims by combining elements of multiple photographs, known as compositing. The above black and white image of the National War College, in Washington, D.C., is an example of this.
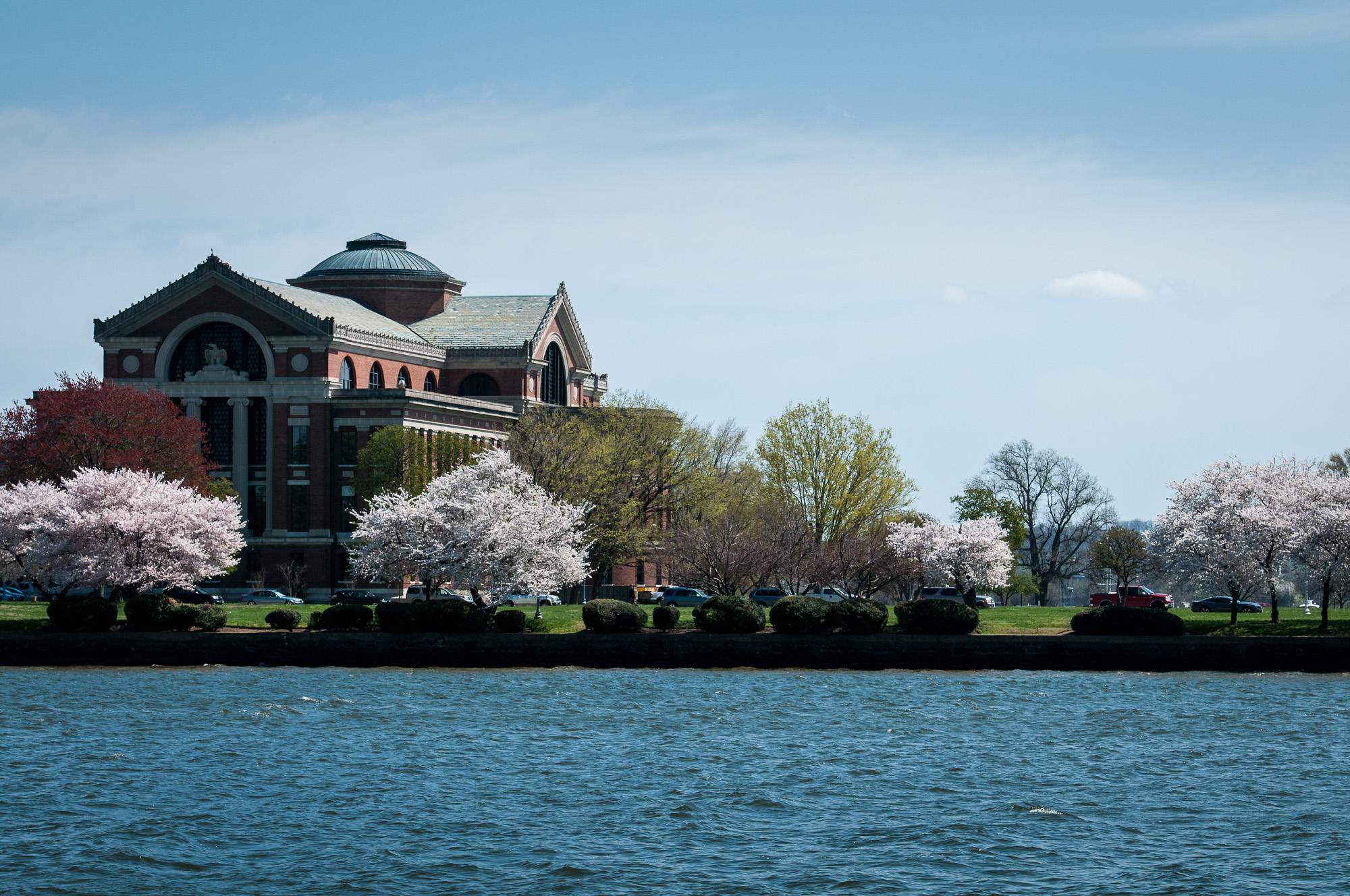
These images were created in the spring, when the cherry blossoms were in full bloom. My brother and I were hiking around East Potomac Park, seeing what it had to offer. Near the end of the park you can see the National War College across the Washington Channel, near where the Anacostia River enters the Potomac. It was almost noon, and not very cloudy, so the light was a bit harsh. You can see from the color image how the scene looked to my eyes.
Color image of the National War College, taken from East Potomac Park, Washington, D.C.
I had an infrared filter with me (see below for details) and thought it might work well. It blocks out visible light and only allows infrared and near-infrared light to reach the sensor. Most digital camera sensors have a filter over them that blocks out most (but not all) infrared light. This means it takes a lot of time for enough light to reach the sensor to create a well-exposed image. When using the IR filter I will usually set the ISO to around 800 to make the sensor more sensitive to light and allow shorter exposure times. In this case, with the ISO set to 800 and the aperture set to f/8, the exposure time with the IR filter was 73 seconds. As you can see in the infrared image, an exposure this long removes all detail from the water. It just looks like a flat grey road. I liked the infrared effect on the trees, building, and sky, but not on the water.
Black and white infrared image of the National War College, taken from East Potomac Park, Washington, D.C.
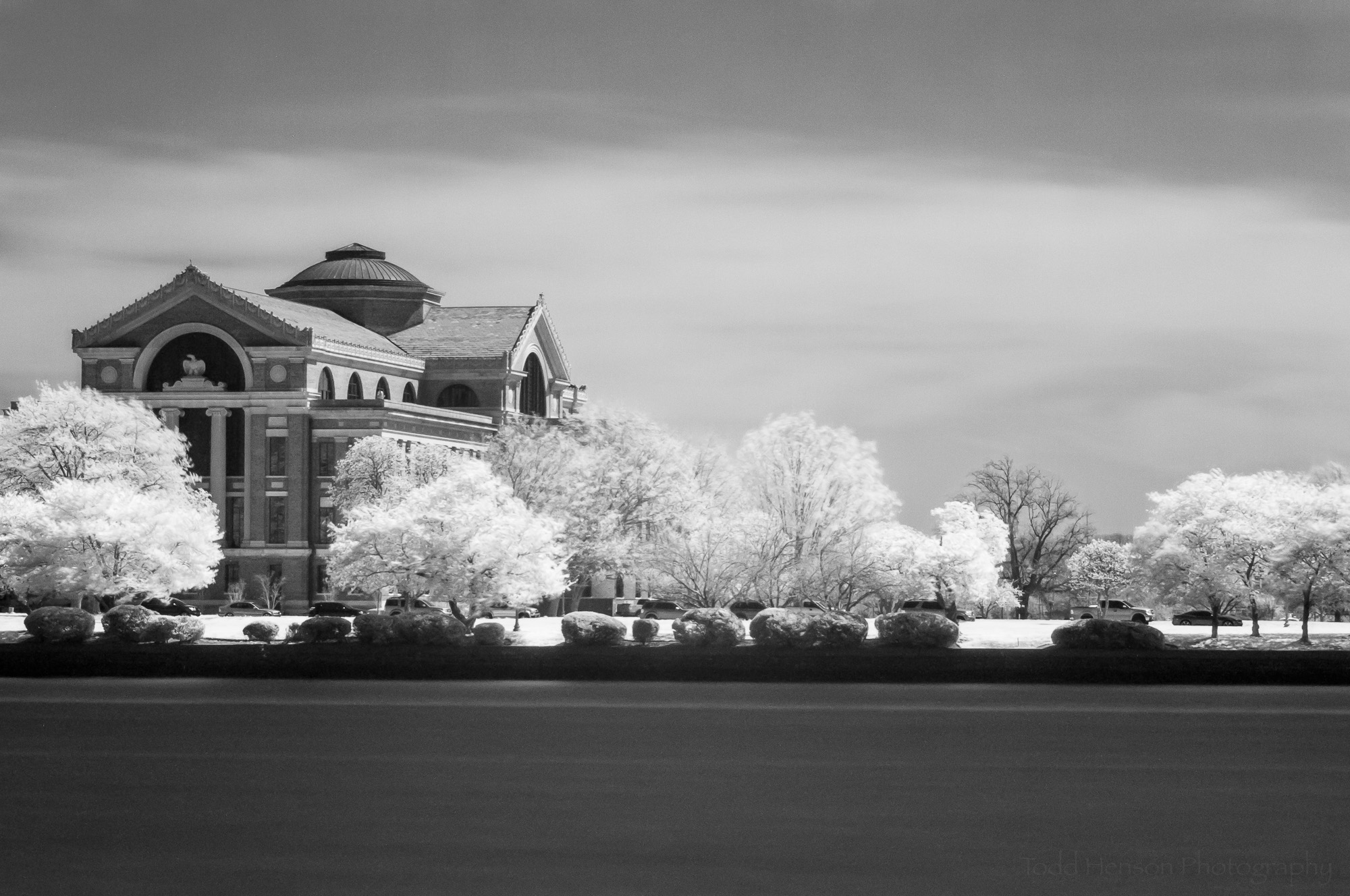
I made sure to capture images both with and without the infrared filter. This gave me something to work with when in Lightroom and Photoshop. To process the images I converted the color image to black and white, paying attention to the water. When I had the water the way I wanted it I selected the black and white image and the infrared image and told Lightroom to open those in Photoshop as layers.
Black and white image (converted from the color image) of the National War College, taken from East Potomac Park, Washington, D.C.
Turns out I had slightly moved the tripod between creating the color image and infrared image, so they didn’t perfectly line up. I was able to correct this in Photoshop by using auto-align layers and cropping off any excess. In this way Photoshop assured both images were perfectly lined up.
The top layer was the black and white image, converted from color. This is the image with the water the way I wanted it to look. The bottom layer was the infrared image. I created a layer mask on the top layer and painted black on the mask. This revealed the layer below where I painted. At first I set the layer mask opacity to about 50%, so I was painting in 50% of what was below, meaning I had an interesting combination of the two. I used this on the entire upper portion of the image, everything except for the water. Then I bumped up the opacity to 100% for the trees and sky, allowing the infrared image to show through completely for those portions of the image. Because I never brushed anything on the water, it remains completely from the black and white image.
Click through the images below to see the bottom layer (infrared), top layer (black and white), and finally all layers with the layer mask applied (the composite).
When I was finished I saved the image, which imported it back into Lightroom, giving me four images. The first is the original color image. The second is the black and white conversion from the color image. The third is the infrared image. And the fourth is the Photoshop composite of the black and white and infrared images. I performed a couple more small tweaks to the composite in Lightroom, then called it finished.
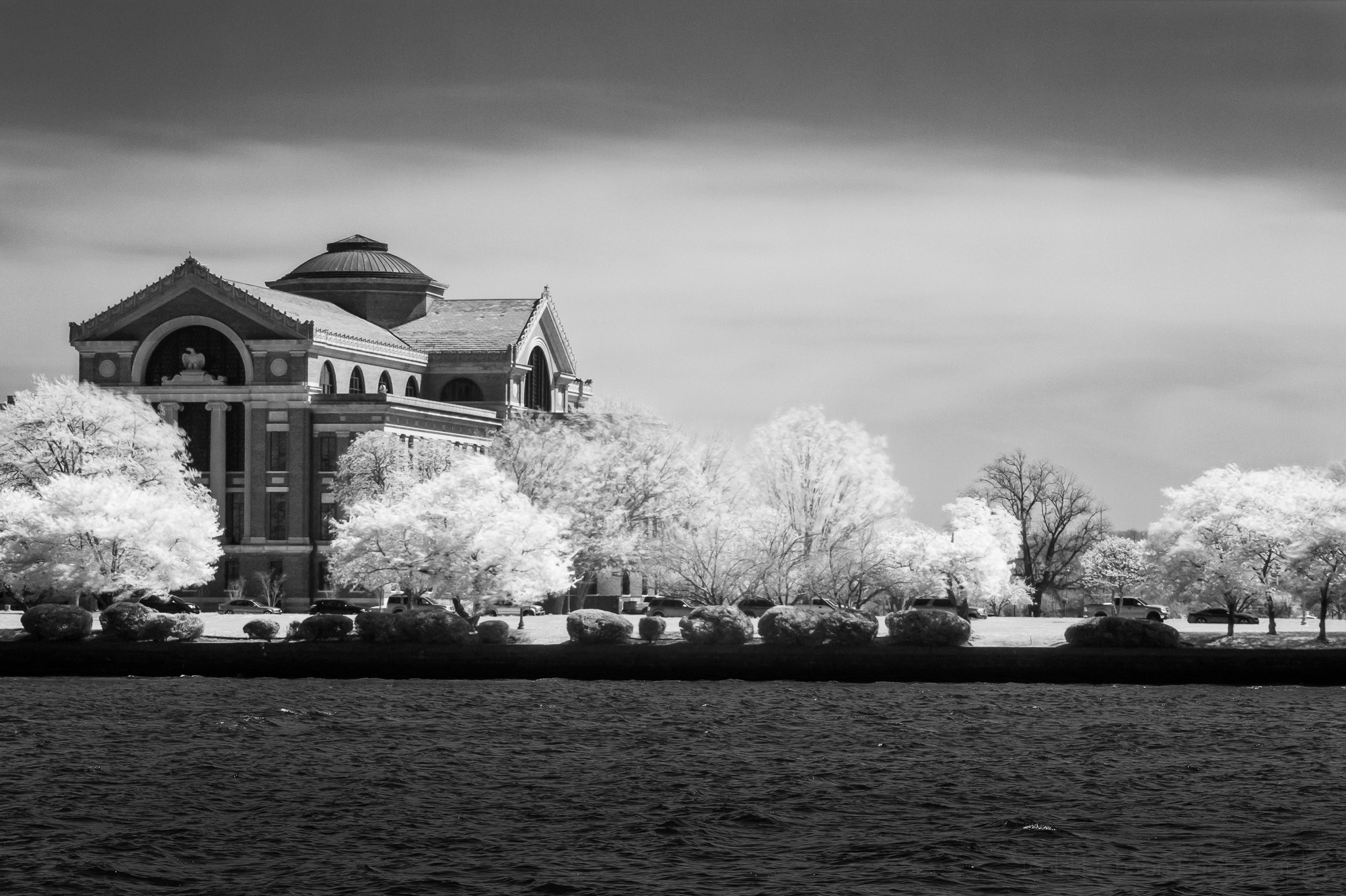




In the final composite image, the water is from the black and white image, allowing me to show the texture of the water. The sky and trees are from the infrared image. Infrared gives a very unique glow to sources of heat, such as trees. And the building is a combination of the black and white and the infrared images.
The infrared filter I used to create these images is a Singh-Ray I-Ray 830 Infrared filter. It blocks out all visible and ultraviolet light, letting through only pure infrared light. When used with most cameras this filter will require fairly long exposure times, but it can add an interesting look to an image. I really enjoy experimenting with it, seeing how it affects the image in different environments. It’s a great creative tool.
Do you enjoy these posts?
Sign up to receive periodic emails with updates and thoughts. Don’t worry, I won’t spam you. And please consider purchasing artwork or products from my online store, and using my affiliate links in the sidebar to the right when shopping online.
I appreciate your support!